
Hydroxides are slightly soluble with the alkaline earth metals.

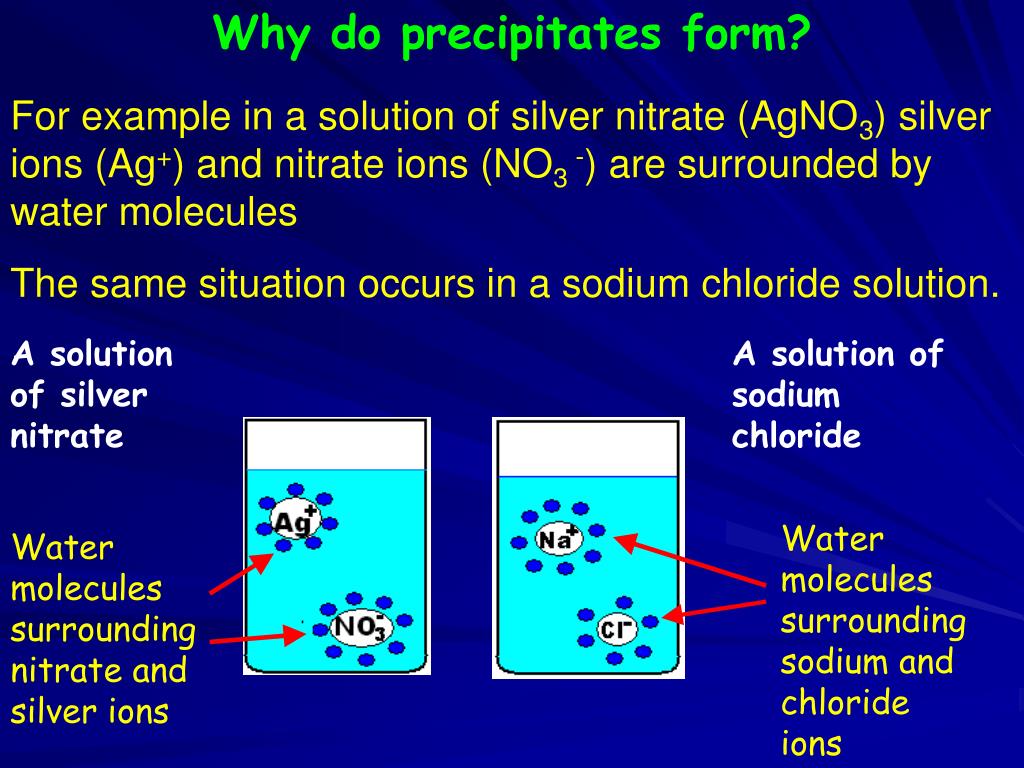
So the reaction including all components would be:ĪC(aq) + BD(aq) –> AD(s) + B +(aq) + C –(aq)ĪgNO 3(aq) + NaCl (aq) –> AgCl(s) + Na +(aq) + NO 3 –(aq)īecause the reactants are aqueous and we want to know the ions in solution, it is common to write the reaction in terms of the ions. The reactants must be ionic compounds in solution. The most general form of a precipitation reaction then is: The product must include a solid product. The reactants are usually two or more ionic aqueous molecules.
#WHEN WILL A PRECIPITATE FORM HOW TO#
How to Identify a Precipitation ReactionĪ precipitation reaction will always have a solid product. These reactions are commonly used to help determine what ions are in the solution. The liquid left behind is referred to as the supernatant. The solid particles can then also be removed from the solution by various means such as filtration, decantation, centrifuging. In precipitation reactions, the formed precipitate can remain suspended in solution or may sink to the bottom. AB and CD are both ionic compounds aqueous in solution. To be a precipitate reaction, either AD or CB will be an insoluble solid. This type of reaction takes the following form. The other pair of cation and anion may or may not be soluble. That is when there are two salts that are soluble, and when the cation of one binds with the anion of the other it forms a solid product that is not soluble. Often, a precipitation reaction is a ‘double replacement reaction’. Lead iodide precipitating out of solution as a solid compound (from Wikipedia Commons)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
